Public goods and social welfare
The Quiz on Public Goods and Social Welfare is an interactive study material that supports the study on social welfare produced by the project "Fresh-up Economics. Towards Economic Literacy in Europe".
The "Fresh-up Economics" project aims to integrate socio-economic issues into adult education by providing adult educators with information and teaching materials to increase their competence to promote learning on socio-economic issues.
Put your knowledge of public goods and social welfare to the test. The quiz contains 10 questions with multiple choice answers and 10 explanatory short stories.
The contents of the quiz are the sole responsibility of the Peipsi Center for Transboundary Cooperation and can in no way be taken to reflect the views of the program, the countries participating in the program or the European Union.
The #Freshupeconomics project has been funded with support from the European Commission. Its contents and material reflect the views only of the author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein. Project code: 2019-1-DE02-KA204-006534.
In what order should needs and desires be met in order to increase human well-being?
In what order should needs and desires be met in order to increase human well-being?
The goal of the state is to increase the social welfare of its citizens. If the state wants to achieve this goal, the distribution of what type of goods should it organize?
The goal of the state is to increase the social welfare of its citizens. If the state wants to achieve this goal, the distribution of what type of goods should it organize?
Name the purpose of social welfare.
Name the purpose of social welfare.
In order to increase social welfare, a liberal welfare state prioritizes economic growth that allows citizens to work and create their own well-being. Which of these countries is guided by liberal ideas?
In order to increase social welfare, a liberal welfare state prioritizes economic growth that allows citizens to work and create their own well-being. Which of these countries is guided by liberal ideas?
A system that seeks to increase social welfare by eradicating poverty and promoting social equality is called…
A system that seeks to increase social welfare by eradicating poverty and promoting social equality is called…
Which institution is the main provider of welfare services in the corporate-conservative system?
Which institution is the main provider of welfare services in the corporate-conservative system?
In a market economy, public and common goods are produced less than society wants. What is the reason for this?
In a market economy, public and common goods are produced less than society wants. What is the reason for this?
How should the ‘free riders’ problem’ be solved according to neoclassical economic theory?
How should the ‘free riders’ problem’ be solved according to neoclassical economic theory?
What is explained by the expression ‘tragedy of the commons?
What is explained by the expression ‘tragedy of the commons?
Countries use the gross domestic product (GDP) to measure well-being. What GDP measures?
Countries use the gross domestic product (GDP) to measure well-being. What GDP measures?
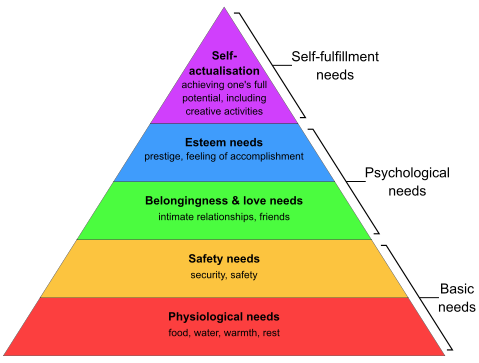
Well-being can be achieved by satisfying societal needs and / or eliminating peoples’ unnecessary desires. According to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, human well-being is based on physiological (food, water, air, sleep, etc.) and safety needs (physical and financial safety, job security, health) being met. These two groups of needs are also called basic needs. When basic needs are satisfied, a person strives for realizing their social needs. We all look for social connections with friends and family and want others to respect us. In doing so, we try to increase our self-esteem and self-confidence. Self-realization is the realization of one's full potential. This is the highest level of the hierarchy that we strive for.
Most goods that people typically think about are private goods (rival and excludable). Private goods are, for instance, mobile phones, clothes, cars, fridges, watches, consumer goods, and private services such as hairdressing and beauty services, etc. The distribution of private goods takes place on the market, as a result of supply and demand.
Club goods (excludable, non-rival) are, for example, Wi-Fi, Internet, satellite TV, private parks, private roads, etc.
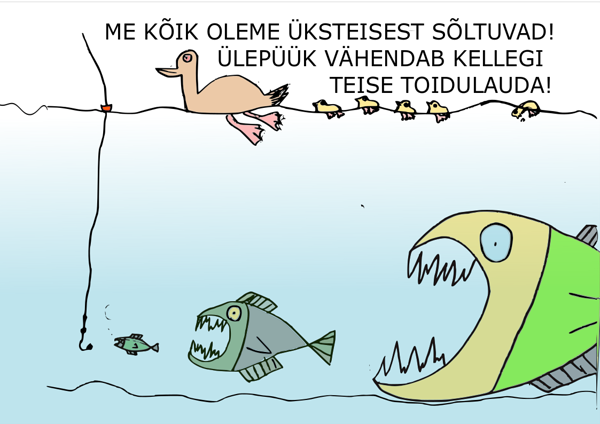
Common good (non-excludable, rival) is for example wild fishing. If one person catches fish from a public lake, it is impossible to prevent others from fishing in the same place; the more one person catches, the lower the chances of others to get fish.
Public good (non-excludable, non-rival) is for example national defence. From military attacks, it is not possible to protect only those people who have paid for national defence and at the same time, the addition of one protected person does not weaken the protection of others.
Public and common goods are a market failure. This means that the market cannot distribute these goods and public intervention is needed. How governments organize the distribution of public and common goods depends on the government's policy approach to social welfare.
Social welfare is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic needs. Often welfare is used as synonymous with social security but actually, social security includes a governmental support system only for sickness, accidents at work, incapacity for work, and unemployment. Welfare-related instruments can be both allowances and services. A country that takes responsibility for social welfare is called a welfare state.
The aim of a liberal system is to create a situation where everyone who can be an entrepreneur or do paid work would do so and ensure their own well-being. Social benefits do exist, but in most cases, they only cover the needs of the low-income working class. In a liberal welfare state, both poverty and social stratification are high.
The social-democratic welfare system is equal in its purpose and conspicuously universal in its political style. This system is characterized by high social spending, decommodification of social rights, and social stratification. The state is also involved in caring for children, the elderly, and the helpless. Thus, all residents of the country are connected to one universal insurance system, from which everyone receives earning-based support and, where everyone has the same rights regardless of status or gender. Such a system creates solidarity with the state among the citizens because everyone depends on the state, they also feel obliged to pay taxes to maintain the system.
In a corporate-conservative system, the role of the market economy is not seen as a potential guarantor of prosperity, nor is the guarantee of social rights necessary to achieve prosperity. Maintaining differences in status dominates, rights are linked to class and status, and the redistributive effect of the state is not considered significant. The preservation of traditional family values and the influence of the church are considered important. Thus, the main provider of care is the family. State intervention consists in distributing financial support to families who have to ensure the functioning of welfare services. Social security excludes unemployed women, but mothers have family benefits. Kindergartens and other care facilities are generally underdeveloped. The role of private insurance benefits is only marginal.
The reason for the lower production of public and common goods is the fact that their consumption is accompanied by the so-called ‘free-riders’ problem’. The ‘free-riders’ problem’ is a type of market failure that occurs when those who benefit from goods or services do not pay or under-pay for them. At the same time, it is impossible to exclude non-payers from accessing or using these goods. Thus, the public and common goods may be under-produced, over-used or become degraded.
Furthermore, if the marginal cost of serving one more customer is essentially zero, it is socially optimal to offer the product at a zero price. Therefore, producing public goods is not a business model, which is why private markets do not have an incentive to provide them.
Economists suggest two ways to address the free-rider problem and the problem of external cost:
● According to the Neoclassical approach, the government should organize the conversion of public and common goods into private goods.
● According to the Keynesian approach, the government should organize the distribution of public and common goods itself, using various ‘command-and-control’ measures.
The decision as to how the government should intervene in the provision of public and collective benefits should be based on an analysis of whether the benefits of consuming these benefits outweigh the costs to society of taxation. However, such an analysis is not always carried out but is a matter of political decision.
As public and common goods have no supply in the market sense, their price is not formed on the market. There is a demand for these goods in society, as a result of which the value of these goods can be assessed. The higher the value of these goods in society, the greater the demand and the greater the pressure on the consumption of these goods, which ultimately leads to the over-consumption of public and public goods. Such a situation was explained by G. Hardin (1968) as a ‘tragedy of the commons’. It is an economic problem where everyone has an incentive to consume a resource at the expense of other people. This results in over-consumption, under-investment and final depletion of the resource.
Allikas: Wikipedia. Resource depletation.
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the sum of the prices of the total production of economic goods and services (hereinafter also economic goods) produced in one country during the year. Economic goods are goods and services that are of benefit to society, they are deficient to some extent and have opportunity costs. Economic goods include for example bread, car, house, computer, fuel, but also various services such as beauty services, etc. For the country's population, GDP growth means better access for people to economic goods and services and the opportunity to improve their standard of living. Despite its widespread use, GDP is not a suitable indicator for measuring well-being.















_block.jpg)




